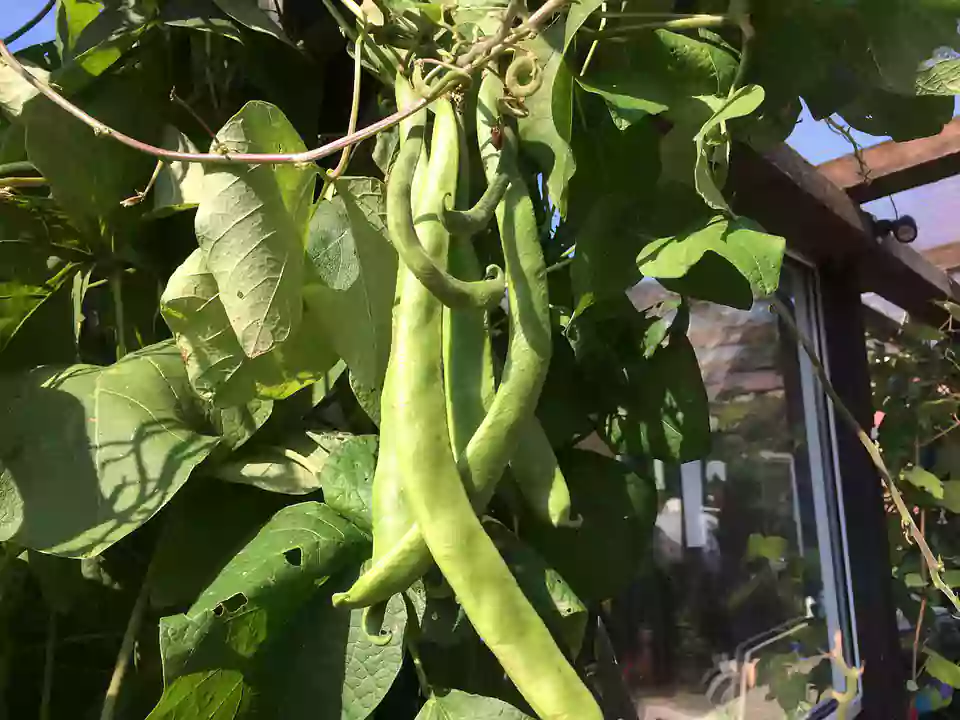
Green beans are growing, but no beans
String beans and snap beans are other names for the fragile annual vegetable known as green beans (Phaseolus vulgaris). In your vegetable garden, green bean plants can develop quickly and produce many harvestable beans that are simple to care for. In this article, we are going to talk about growing green beans.
Table of Contents
Why Do My Green Beans Have No Beans?
There won’t be any bean pod development if the soil dries up excessively between irrigations or downpours. Even though mulch can assist, hot, windy days can still cause plants to dry out. Mulch may work well with higher crops upwind to provide wind protection.

Why Are Green Beans Flowering Early?
If you reside in one of the southern states with sandy soil, it may be root-knot nematodes; in that case, plant some marigolds where you intend to grow beans the next year. Along with the beans, marigolds are beneficial to plant. I would advise using sun hemp to cover the entire garden over the summer, using it as green manure, and then growing your beans in it in the spring if you have a nematode issue (skip the fall this year).
Sunn hemp can be cut with a scythe and then used as mulch if you don’t have a way to get it thoroughly tilled in. But the most typical problem for what you’re saying is that they may have been overfertilized. Beans grown in fertile soil won’t fix nitrogen, so rather than growing tall and producing plenty of beans, they’ll stay short and produce few. If you use a fertilizer with beans, you must exercise extreme caution.

How Long Does It Take For Green Beans To Grow?
Bean plants go through four stages in their growth:
- The new plant is enclosed in a capsule called a seed.
- The young plant’s process that emerges from the seed husk is called germination.
- When the seedling develops its genuine sets of adult leaves, leaf growth begins (as opposed to the immature initial leaf structures).
- The plant is ready to start reproducing after it has reached the flowering stage.
The Green Bean Growing Process
Bean Seed
Various seeds are produced by beans, and each seed is encased in a pod. The pod cracks open in the sun as it dries and gets older on the plants. The seeds can be removed by gardeners for storage or subsequent planting, or they will eventually fall out of the hard, dried pod and land on the ground.
In reality, bean seeds are divided into two parts or cotyledons. The developing plant has a feeding source inside each cotyledon. In fact, young bean plants can survive for a few days on the food that has been stored in the cotyledon before they can access the nutrients in the soil.

Germination Stage
When a seed is at the germination stage, it has just sprouted. When water dissolves or breaks apart the hard shell surrounding the seed or embryo, beans sprout or germinate. Warmth expedites the process. The bean will release a radicle, a little (embryonic) root.
- Split Casing and Root Development
The roots come out of the bean seeds initially once the casing separates. From the seed, roots slowly spread out, searching for moisture and nourishment. As they emerge from the bean seed, the roots resemble white threads.
- During germination, amend the soil.
Beans require nutrient-rich soil, much as all other vegetables. Starting a vegetable garden requires amending the soil and regularly adding new nutrients. When bean seeds are planted in healthy garden soil that has been composted, the roots can quickly locate available nutrients. The roots draw water and nutrients into the seed as they go downward. The seed gradually acquires all it needs to progress to the next phase of its life cycle: leaf growth.

Leaf Growth
A single stem emerges from the bean plant when the seed germinates, and the roots expand. Two little leaves appear as the stalk pokes its head out of the ground. A bean plant’s earliest leaves don’t resemble regular bean plant leaves at all. They are rounded and aid in the plant’s fast development into a robust, mature plant.
As opposed to other plants, which often emerge their leaves below the soil’s surface, these leaves, also known as cotyledons, are attached to the seed.
The seed and cotyledons are securely planted by a stalk (hypocotyl).
The seedling’s initial set of leaves enables photosynthesis. As soon as the adult leaves are created, they start to fall off.
Special cells in the leaves contain chlorophyll, which converts sunlight into energy the plant may use. Warmth, moisture, sunshine, and carbon dioxide are components the plant can use to convert into food for growth and upkeep. New leaves immediately appear, and a complete plant eventually takes shape.

Flowering Period
Flowering marks the culmination of the bean plant’s life cycle. Plants start reproducing as soon as they can produce flowers, which are the reproductive part of the plant. Although the length of time it takes a bean plant to flower varies depending on the variety of beans, in general, you’ll start to notice flowers on the bean plant six to eight weeks after germination. Seed pods form as a result of pollination or fertilization of the blooms.
At the same time that bean plants bloom, they also set mature seed pods. This is typical of plants of the legume family. People either harvest mature seed pods for consumption or leave them on the plant to develop and dry in the sun. Dry bean pods either naturally split over time and release the beans onto the ground or produce beans for cooking or storing. That restarts the bean plant’s life cycle at the seeds, where it started in the first place.

How Do You Induce Flowering Beans?
You require potassium (potash) fertilizer to aid trigger flowering to encourage flowering. Your soil may be nitrogen-rich, allowing you to add nitrogen-rich materials to the soil, such as compost, blood and bone, or sheep pellets, to get the healthy green growth you desire.

FAQ
Why are there no beans on my runner beans?
At the roots is a lack of moisture. Poor soil or growing conditions, including acidic soils with a pH below 6.5, pest or disease issues, frost damage, a lack of nutrients, or an absence of organic matter. Lack of pollinators, possibly due to the cold, wet, or windy weather.
What nutrients promote flowering?
The mineral phosphorus (P) encourages the growth of roots, blooming and fruit production, and disease resistance.
How long after flowering do beans appear?
Bean plants typically grow and yield beans in about two months; however, different varieties mature at different rates. It’s also important to understand how long after flowering, runner beans appear. Depending on the cultivar and climate, the period might last between 45 and 75 days.
Previous Article:Cucumber Seedlings Falling Over? Here’s How To Cure It!